Basically the term cold roof refers to a traditional roof or vented roof while hot roof refers to a roof that is not ventilated and which has foam insulation attached directly to the roof sheathing.
Cold climate vent attic or unvented.
Wind and air pressure move cold air around chilling homeowners.
Vented roofs vented roofs serve a number of different purposes and their roles vary from climate to climate.
People usually vent attics in cold climates to prevent moisture accumulation in the roof sheathing and control ice dams.
In cold climates moisture in roof assemblies typically comes from inside and the key to problems with moisture is the temperature of the roof sheathing.
With unvented attics the air barrier vapor and thermal controls are installed at the roof deck.
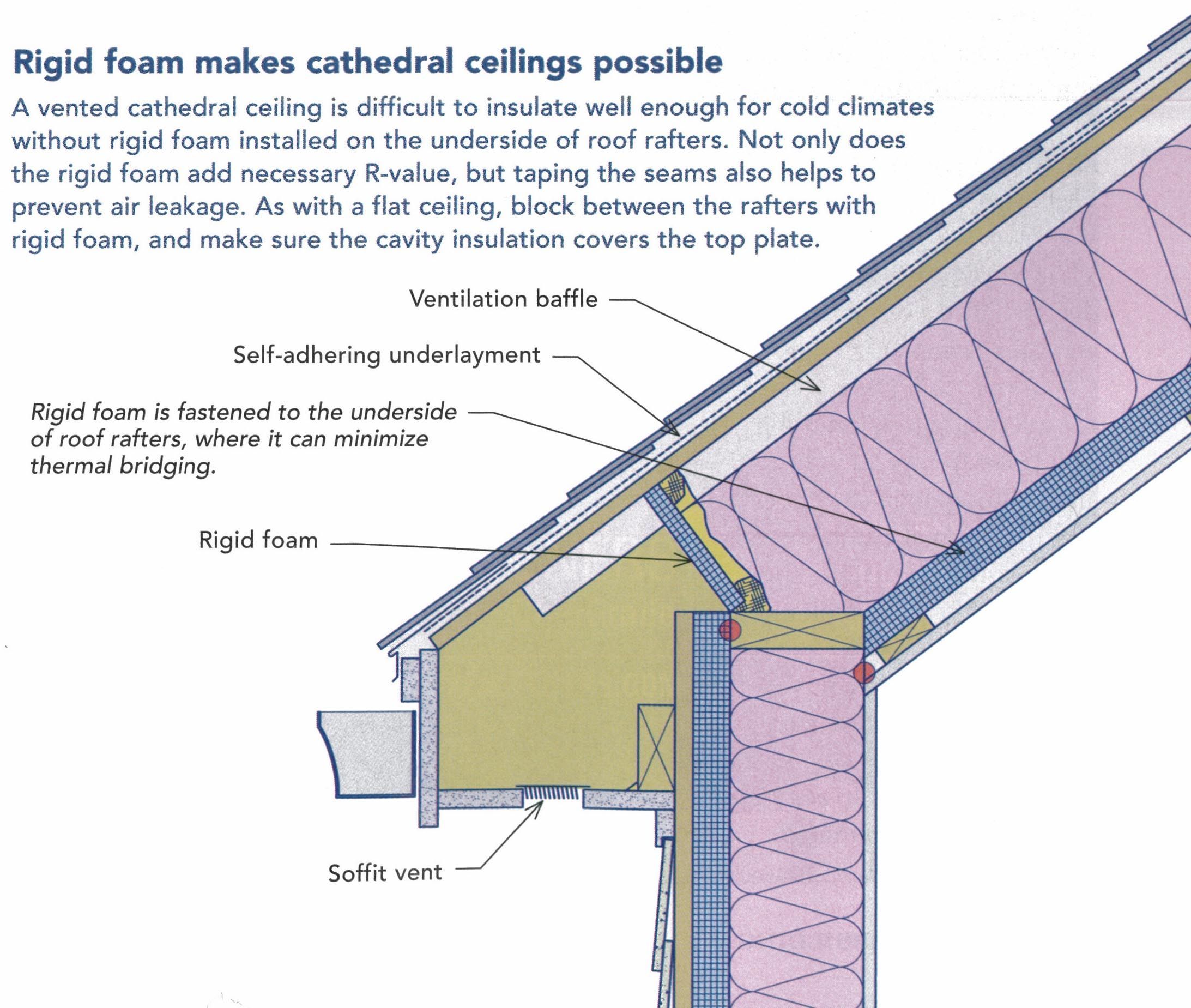
Unvented attics rely on an air impermeable insulation installed to the roof deck s underside i e.
In cold northern climates snow can be blown in through these openings accumulating melting and causing damage to the ceiling or creating the potential premature structural failure or mold growth inside the roof assembly.
A secondary goal is to vent moisture that infiltrates the attic from the conditioned home.
Durability openings in the soffits gables mushroom and ridge vents allow more than just air to enter the attic.
Unvented attic construction is most common in housing and type v construction located in the warm climate zones of 1 through 4 but is suitable for any climate zone.
Attic ceiling to stop airborne moisture from reaching a cold surface and condensing inside the building envelope.
Attic access hatches plumbing chases recessed lights and duct vents all can leak conditioned air making your home less comfortable.
See the irc or the guide unvented attic insulation for details.
For example if an r 80 unvented cathedralized attic is to be constructed in a cold climate a minimum of r 40 50 should be air impermeable insulation installed and layered according to section r806 5 of the 2012 irc figure 4.
In this design insulation effectively separates the interior and exterior spaces while slowing down moisture flow so the dewpoint is not achieved within the building envelope.
If the space conditioning system is located in the attic such as it is in warm locations the energy savings that can be realized are very apparent.